In 2024, the business world is more connected than ever before. Companies of all sizes are leveraging a vast ecosystem of third-party vendors, suppliers, and partners and this interconnectedness, while driving innovation and efficiency, also exposes organisations to a myriad of risks, particularly regarding data security and privacy.
Due to this, controlling data and third-party risk management has become a critical aspect of modern business strategy.
This Harnham blog explores the essential steps and considerations for enterprises aiming to effectively manage third-party data risks.
Understanding third-party risk management
Third-party data risks emerge from the potential security threats and privacy breaches that can arise from sharing sensitive information with external entities. These risks can lead to significant financial losses, legal penalties, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Uber, for example, made headlines in early 2023 when several of their third-party vendors were breached, resulting in the leaking of 80,000+ employee data records, employee communications, and invoices.
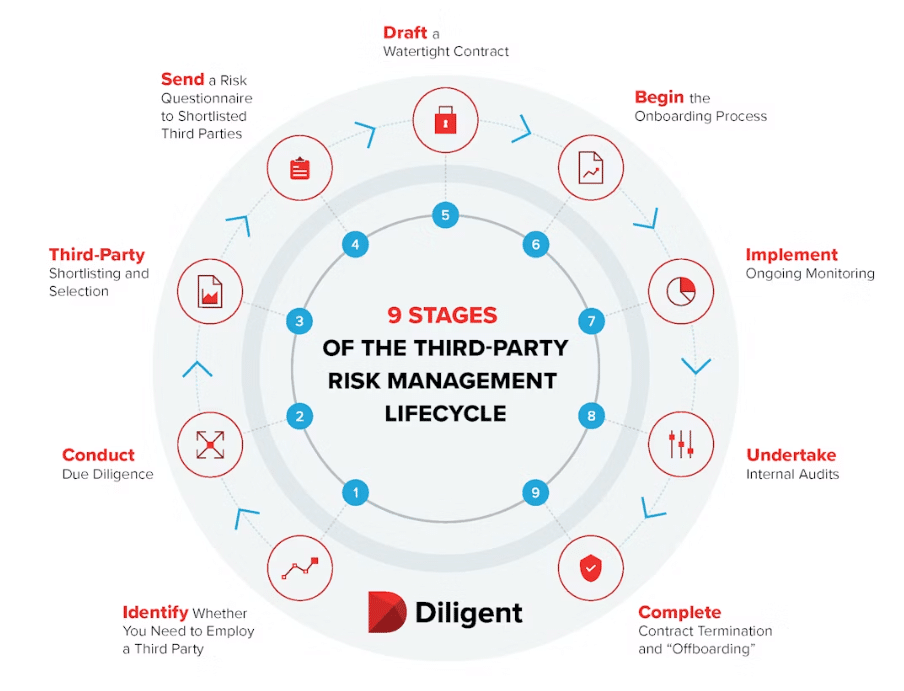
Source: https://www.diligent.com/resources/blog/third-party-risk-management-lifecycle
As regulatory frameworks around data privacy continue to tighten globally, with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, the need for robust third-party data risk management is more pronounced than ever.
How to keep authority and control over your data
Keeping that authority and control over your data, even when in the hands of an outside party, is crucial.
Waseem Ali, CEO of Rockborne, said: “If using a third party to store confidential personal data, at a bare-minimum I would expect that third party to abide my business’ policies and frameworks. I would hope they would go further than this, but this would be my minimum expectation.
“Whether your organisation is able store data with a third-party provider will also depend on the industry you are operating in – certain industries may have specific requirements or frameworks to abide by. For example, in some the storing data with an outside actor will not be allowed and others may not tolerate data being stored anywhere outside of the UK.
“As a data leader, my biggest concern when using third parties is the minute that the data leaves the organisation, because it then falls out of my control. And ultimately, whether it is in or outside of my control, I still retain liability of that data.
“Therefore, if a third party requires access because they are working with me as a consulting organisation for example, I would typically enforce a rule where they use our hardware, systems, and infrastructure. I want them to work in our environment using one of our laptops or a remote desktop, so that I retain authority of, and control over, the risk.”
Understanding third-party relationships
In managing third-party relationships, enterprises in 2024 face an evolving landscape that’s heavily data-driven. The interconnectivity of services means that data flows through various channels, necessitating a robust framework for third-party risk management. A critical aspect is the comprehensive evaluation of data security practices of third-party vendors to ensure they align with the enterprise’s standards and regulatory requirements.
To foster secure data exchange, enterprises must establish clear data handling and sharing protocols. Implementing stringent data access controls and regular audits can significantly mitigate potential risks. Additionally, the advent of technologies like blockchain and advanced encryption methods offers new avenues for securing data transfers, ensuring integrity and confidentiality.
Moreover, in this digital age, the importance of real-time monitoring cannot be overstated. Leveraging advanced analytics and AI-driven tools enables enterprises to detect potential data breaches and vulnerabilities in real-time, enhancing the responsiveness to threats within the third-party ecosystem.
Understanding the criticality of these relationships, The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides updates & guidelines that serve as a benchmark for third-party risk management, emphasizing the importance of data security in vendor relationships.
Similarly, The International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP) offers resources and frameworks to help navigate the complexities of data privacy and protection in third-party engagements, ensuring that enterprises stay ahead in the management of third-party risks in 2024.
Compliance Risks
Compliance risks in third-party risk management have also become a critical concern in 2024. As organizations navigate through complex regulatory environments, ensuring third-party compliance is not just about avoiding penalties but is integral to maintaining trust and reputation.
The GDPR and CCPA are examples of regulations that have heightened the focus on data privacy and security, emphasizing the need for stringent compliance measures.
By incorporating robust compliance checks and balances in their third-party risk management strategies, businesses can protect themselves against legal ramifications and safeguard their brand integrity. This approach not only aligns with regulatory demands but also fortifies the enterprise’s commitment to ethical practices and data protection.
Navigating Financial & Reputational Risks
In the wake of stringent regulations like the GDPR and CCPA, the landscape of third-party risk management is becoming increasingly complex, intertwining the need for regulatory compliance with the management of financial and reputational risks in 2024.
As businesses strive to adhere to these compliance measures, the emphasis shifts towards a comprehensive approach that extends beyond legalities to encompass the financial and reputational dimensions of third-party engagements.
Leveraging advanced technologies for predictive risk assessment and real-time monitoring, organizations aim to uphold ethical standards and data protection, ensuring a robust defense against potential financial setbacks and reputational harm. This nuanced approach not only mitigates the immediate concerns around compliance but also addresses broader implications for an organization’s financial health and reputation.
As the digital ecosystem expands, so does the array of risks, from data breaches impacting customer trust to financial losses from operational disruptions. The integration of technologies like AI and machine learning into risk management strategies offers a proactive stance, enabling businesses to anticipate challenges and adapt swiftly.
This dynamic, forward-looking strategy, underpinned by a commitment to ethical practices and data protection, is essential for maintaining competitiveness and integrity in today’s market.
Leveraging Security Ratings
For third-party risk management in 2024, leveraging security ratings is pivotal for enhancing organizational security and transparency within vendor networks.
These ratings provide invaluable insights into the cybersecurity postures of third-party vendors, thereby informing risk assessments, vendor selection, and ongoing monitoring efforts.
The integration of security ratings into third-party risk management frameworks enables businesses to stratify vendors based on their security performance, facilitating a more informed and dynamic approach to managing third-party relationships.
This strategy not only aids in mitigating potential security vulnerabilities but also bolsters compliance with regulatory standards, protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of digital assets in an interconnected business landscape.
Managing Operational risk
In 2024, operational risks in third-party risk management are a critical focus for data-centric businesses like those Harnham partners with.
This shift underscores the heightened importance of maintaining not just the security but the operational integrity of data flows and systems that are increasingly outsourced or managed through third-party relationships.
The convergence of operational risks with third-party engagements necessitates a strategic approach to ensure that these external partnerships do not become the weak link in the data security and compliance chain.
Mitigating these operational risks involves rigorous third-party operational risk management, focusing on ensuring that vendors and suppliers uphold the highest standards of data security and system reliability.
This requires comprehensive due diligence and risk assessments tailored to the specific challenges of managing vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal and financial information.
By integrating rigorous vendor risk management practices and adopting a lifecycle approach to third-party engagements, organizations can safeguard against disruptions, data breaches, and system failures that could jeopardize critical data assets.
Moreover, the advent of new regulations and the rapid pace of technological change have made it imperative for companies to continually monitor and reassess their third-party risk strategies.
Leveraging advanced risk management solutions that offer real-time insights into vendor performance and potential vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining operational resilience in the face of evolving threats.
Our 2024-25 Data and AI Salary Guide is now live!
Take part in the survey today and be in with FIVE chances of winning a £100 Amazon voucher, as well as an intensive one-day AI course courtesy of Rockborne!
UK Survey
US Survey
FR Survey
NL Survey